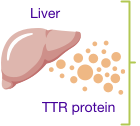
TTR is a protein made mostly in the liver
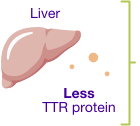
ONPATTRO decreases the amount of TTR protein made in the liver
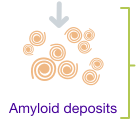
A change in the TTR gene causes the TTR protein to cluster and form amyloid deposits
This helps to decrease the amount of amyloid deposits and may result in fewer symptoms
Amyloid deposits build up in different parts of the body, leading to symptoms of hATTR amyloidosis

ONPATTRO
infusion
TTR is a protein made mostly in the liver
ONPATTRO decreases the
amount of TTR protein made
in the liver
A change in the TTR gene causes the TTR protein to cluster and form amyloid deposits

This helps to decrease the amount of amyloid deposits and may result in fewer symptoms
Amyloid deposits build up in different parts of the body, leading to symptoms of hATTR amyloidosis

ONPATTRO
infusion
TTR protein was reduced by an average of 84% after 18 months in a study of adults with polyneuropathy caused by hATTR amyloidosis who were treated with ONPATTRO.
How ONPATTRO was studied
The safety and effectiveness of ONPATTRO were evaluated in an 18-month study of 225 adult patients with polyneuropathy caused by hATTR amyloidosis.
During the study, some patients received ONPATTRO and their results were compared with those of patients who received a placebo.
The clinical study focused on changes in nerve function and quality of life at 18 months
Nerve function was assessed using a scale called mNIS+7, which measured strength and sensation in the hands, feet, arms, and legs; reflexes; and blood pressure upon standing.
Quality of life was evaluated using the Norfolk QoL-DN questionnaire, which asked patients about the severity of their polyneuropathy symptoms, how often they experienced them, and what impact they felt they had on their daily lives.
The effects of ONPATTRO on other aspects of the disease, including walking ability, nutritional health, and ability to perform activities of daily living, were also evaluated.
From the start of the study to 18 months, nerve function and quality of life significantly improved for patients who received ONPATTRO compared with those who received placebo
ONPATTRO significantly improved
nerve function and quality of life
NERVE
FUNCTION
QUALITY
OF LIFE
Patients who received
placebo got worse
NERVE
FUNCTION
QUALITY
OF LIFE
At 18 months:
56% of patients who received ONPATTRO regained some nerve function from the start of treatment, compared with 4% of those who received placebo
51% of patients who received ONPATTRO reported better quality of life from the start of treatment compared with 10% of those who received placebo
At 18 months:
For patients who received ONPATTRO and did not regain some nerve function, progression of their neuropathy was slowed compared with those who received placebo
ONPATTRO significantly improved
nerve function and quality of life
NERVE
FUNCTION
QUALITY
OF LIFE
Patients who received
placebo got worse
NERVE
FUNCTION
QUALITY
OF LIFE
At 18 months:
56% of patients who received ONPATTRO regained some nerve function from the start of treatment, compared with 4% of those who received placebo
51% of patients who received ONPATTRO reported better quality of life from the start of treatment compared with 10% of those who received placebo
For patients who received ONPATTRO and did not regain some nerve function, progression of their neuropathy was slowed compared with those who received placebo
Other improvements seen by patients who received ONPATTRO during the study
After 18 months of treatment, when compared to patients who received placebo, patients who received ONPATTRO experienced:
Decrease in neuropathy symptoms
Including diarrhea, constipation, dizziness, difficulty urinating, and vomiting
Better nutritional health
Patients treated with ONPATTRO maintained a healthier weight
Increase in walking speed
Patients treated with ONPATTRO maintained a better walking speed
Decrease in pain
Decreased feelings of anxiety and depression
During the study of 225 patients, on average, patients who received ONPATTRO were better able to perform common daily activities compared with those who received placebo
This was assessed by a 24-item questionnaire called R-ODS that asked patients to rate their ability to complete tasks both at the beginning of the study and after 18 months of treatment. Some of these tasks included the ability to:
Take a shower
Walk a full flight of stairs
Turn a key in a lock
Do the dishes
Damage to nerves that affects sensation, movement, strength, and bodily functions such as digestion, urination, and sexual function.
A treatment without any active medication.
The 24-item questionnaire asked patients about their ability to:
- Eat
- Make a sandwich
- Brush teeth
- Wash upper body
- Wash lower body
- Sit on a toilet
- Dress upper body
- Go to the general practitioner
- Read a newspaper or book
- Go shopping
- Travel by public transportation
- Move a chair
- Catch an object
- Bend and pick up an object
- Carry and put down a heavy object
- Walk and avoid obstacles
- Walk outside
- Run
- Dance
- Stand for hours
- Take a shower
- Walk a full flight of stairs
- Turn a key in a lock
- Do the dishes